Consistent Ground-Plane Mapping: A Case Study Utilizing Low-Cost Sensor Measurements and a Satellite Image
Goal
Create a high resolution roadway image for autonomous driving, only using low-cost conventional sensors. The created image should be consistent with the a prior satellite image.
Challenge
Low-cost sensors cannot localize accurately, must resort to matching input and satellite images to achieve consistency, but matching
does not always work.
Example: For the first and second images, I have something to match with. What about the third one? It could (and actually
does) show strong correlation at random wrong location.



Method
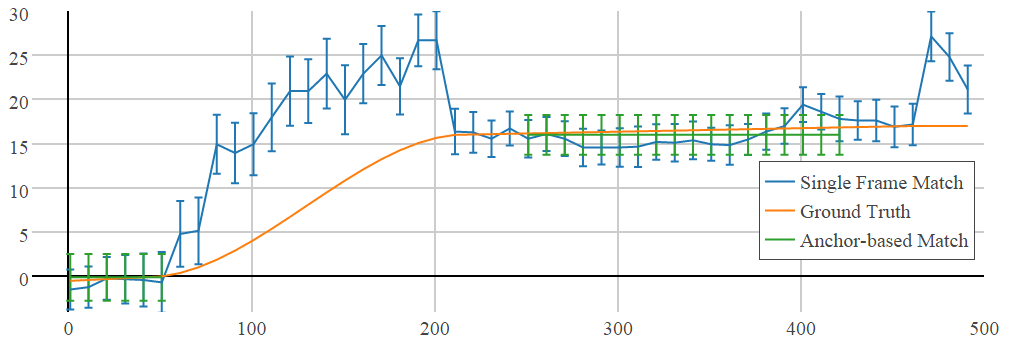
Step 1: Classify anchor frames: frames that have highly identifiable structured textures.
Example: In the above figure, first and second are anchor frames, third is not.
Step 2: Adjacent anchor frames form an anchor, make adjustment in anchor units.
Example: This not only avoids "bad" images, but also produces smooth adjustments.
icra15_demo_HChu_AVu from Hang Chu on Vimeo.